Flow123d
Processes in Fractured Media
Flow123d is a simulator of underground water flow, transport, and mechanical processes in fractured porous media. Novelty of this software is support of computations on complex meshes consisting of simplicial elements of different dimensions. Therefore, continuum models and discrete fracture network models can be combined.
Installation
You have several options when it comes to the installation. You can use our prebuilt Docker images or you can build Flow123d from the source (requires a moderate experience with Linux OS).
For detailed instructions, see the installation guide.
Getting started
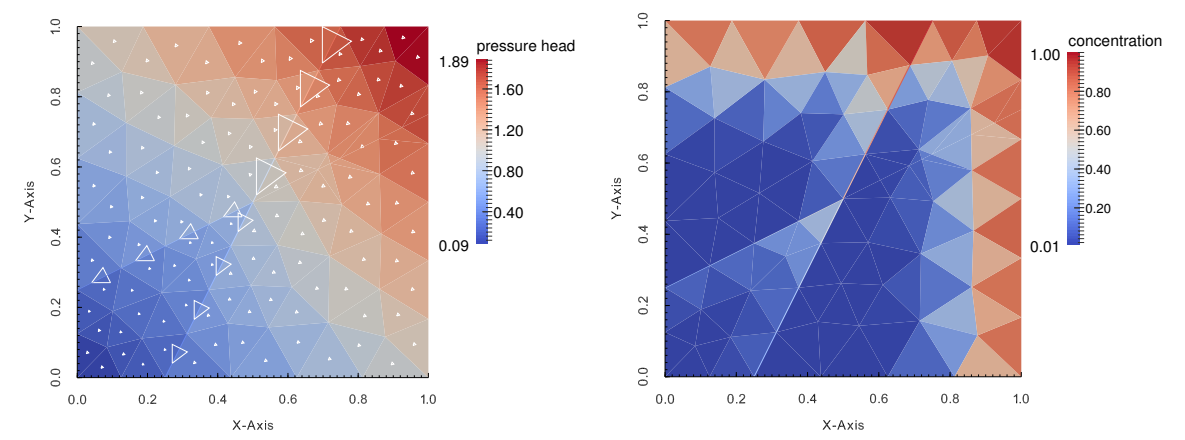
Please refer to the User Guide and Input Reference manual where there is an entire section dedicated to this topic. You can find a step-by-step tutorial explaining geometries, yaml input files
and more. Below you can see a result from the tutorial problem.
Developers
Build
Two step build:
host> bin/fterm # start the Docker developing container
container> make all # produce "build_tree/bin/flow123d"
container> bin/flow123d # launch the simulator using a simple wrapper script
That would start the debug Docker image and build the debug version of the simulator. For the release (optimized) version run:
bin/fterm rel
make all
For details see installation guide or the manual.
Troubleshooting
-
When problem occurs during the compilation process it may be due to a leftover files in a build folder. Cleaning this directory can solve this issue. You can either remove
build-<branch>folder (the folder is located one level above repository root) viamake clean-all, which removes build folders and also remove any symlinks.
To clean all the build folders manually runrm -rf ../build-*while in a repository root.
Runningrm -rfcan quite easily cause a lot of damage, double check that you’re in a correct folder. -
The build tools may fail if the root path contains folders with spaces.
Building the reference manual
The reference manual can be built while staying inside the Docker container
make ref-doc
To copy out reference manual from Docker use command
docker cp.
Singularity
Singularity is a container system targeting HPC applications. Singularity containers can be created from the Docker images and in contrast to Docker they are not allowed to modify system of running containers.
It might be necessary to set a temp directory for large images.
export SINGULARITY_TMPDIR="/some_absolute_path/tmp"
Run simulator in singularity container
singularity exec docker://flow123d/3.1.0 flow123d simulation.yaml
Parallel run, mpiexec out of the image
module add mpich-3.0.2-gcc
mpiexec -host host1,host2 -np 4 singularity exec docker://flow123d/3.1.0 flow123d simulation.yaml
Build
host> git clone https://github.com/flow123d/flow123d.git # clone flow123d repository
host> singularity shell -B flow123d/:/flow123d docker://flow123d/flow-dev-gnu-rel:3.1.0 # starts developing container
container> cd /flow123d
container> make all # produce "build_tree/bin/flow123d"
container> bin/flow123d # launch the simulator
Docker images
Hosted on dockerhub under organization flow123d.
production images
tagged by the release version (e.g. 3.9.0)
-
flow123-gnu- based on gnu libraries and tools
flow123-intel: based on intel libraries (intelmpi, mkl, intel compilers)
alfa images
built by CI, tagged by {branch}-{commit}
ci-gnuci-intel

